|
BOOK NOW |
ASK ABOUT YOUR PAIN |
Home > Blog > Physiotherapy > Conditions > Shoulder Pain Physio > Rotator Cuff Injury > Rotator Cuff Injury Exercises and Physiotherapy
Rotator Cuff Injury Exercises and Physiotherapy
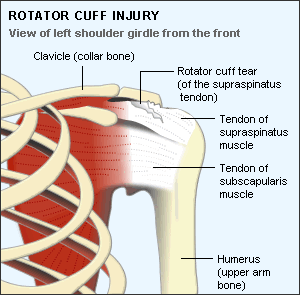
Rotator Cuff Injuries are common shoulder injury that is treated by physiotherapists.
Our shoulder rotator cuff consists of four main muscles and their tendons that works closely together
- the subscapularis
- the supraspinatus
- the infraspinatus and
- the teres minor
Together, they form the rotator cuff and it basically acts as an anchor for your shoulder, stabilizing the humeral head.
Are there different types of rotator cuff damages and injuries? What are they?
As there are a few structures involved in the rotator cuff, it then becomes prone to several types of injuries, which are listed here:
- Rotator cuff inflammation
if or when any of the tendons of the four muscles become inflamed due
to physical stress or direct trauma, tendonitis happens.
Inflammation and tendonitis causes swelling which increases the internal pressure and this can compress on other structures in the shoulder joint - Shoulder impingement syndrome - impingement simply means that a tendon of one of the four rotator cuff muscles becomes impinged, compressed or squeezed
- Calcification of the rotator cuff tendonitis
- sometimes, calcium gets deposited in the tendons of the rotator cuff
(especially do in long term tendonitis cases), causing them to become
hard (calcification) which causes pain as tendon glides with any
movement
- Shoulder bursitis - the shoulder joint has a bursa
which is located just beneath our acromion – this is called the
subacromial bursa, and it can become inflamed if the shoulder is
overused
- Rotator cuff tears - can happen when one
of the tendons or the muscles of the rotator cuff gets stretched beyond
what it can bear, and it tears.
Tears can be partial or complete rupture. Tears happen usually from strong impacting forces such as road traffic accidents or falls, but they are also sometimes caused by gradual tears and micro-tears due to normal wear and tear as we age and use our hands.
What causes a rotator cuff injury?
Our shoulder is very easily injured as we use it all the time in almost every single thing we do, including
- carrying
- lifting
- pulling stuff
- driving cars
- using tools
– these are but some of the activities that require our shoulders to exert force.
Also, traumatic incidences such as falls or road traffic accidents are common-occurring situations which can lead to a shoulder rotator cuff injury.
How do I know I have a rotator cuff injury?

Usually, people with injuries to their rotator cuff often get pain and tenderness in their shoulders, and sometimes their ache and pain can travel down the back of their hand.
Most of the time, the pain is very specific to shoulder-based movement such as reaching up to take something or pulling on a weighted object.
Our patients also often mention that they feel a “baseline ache”, and moreso if they put pressure on their affected shoulder.
Weakness and limited mobility is another common sign.
One thing to note is that if your pain comes as slow and gradual, it’s likely to be caused by wear and tear or tendinitis; but if you get the sudden, sharp ones, it’s likely due to a micro-tear in your rotator cuff.
How can our senior physiotherapists help a patient with rotator cuff injuries?
When you injure your rotator cuff, it’d be best you visit your physician who will refer you to an orthopedic surgeon who will advise you on the severity of the rotator cuff injury, and the options you have.
Most of the time if you have a complete rupture, you would have to undergo surgery to correct the problem.
However, if what you have is a micro-tear or partial-tear, the orthopedic surgeon may advise for conservation management (meaning no operation) and to undergo physiotherapy to maximize range, function and strength as your rotator cuff heals.
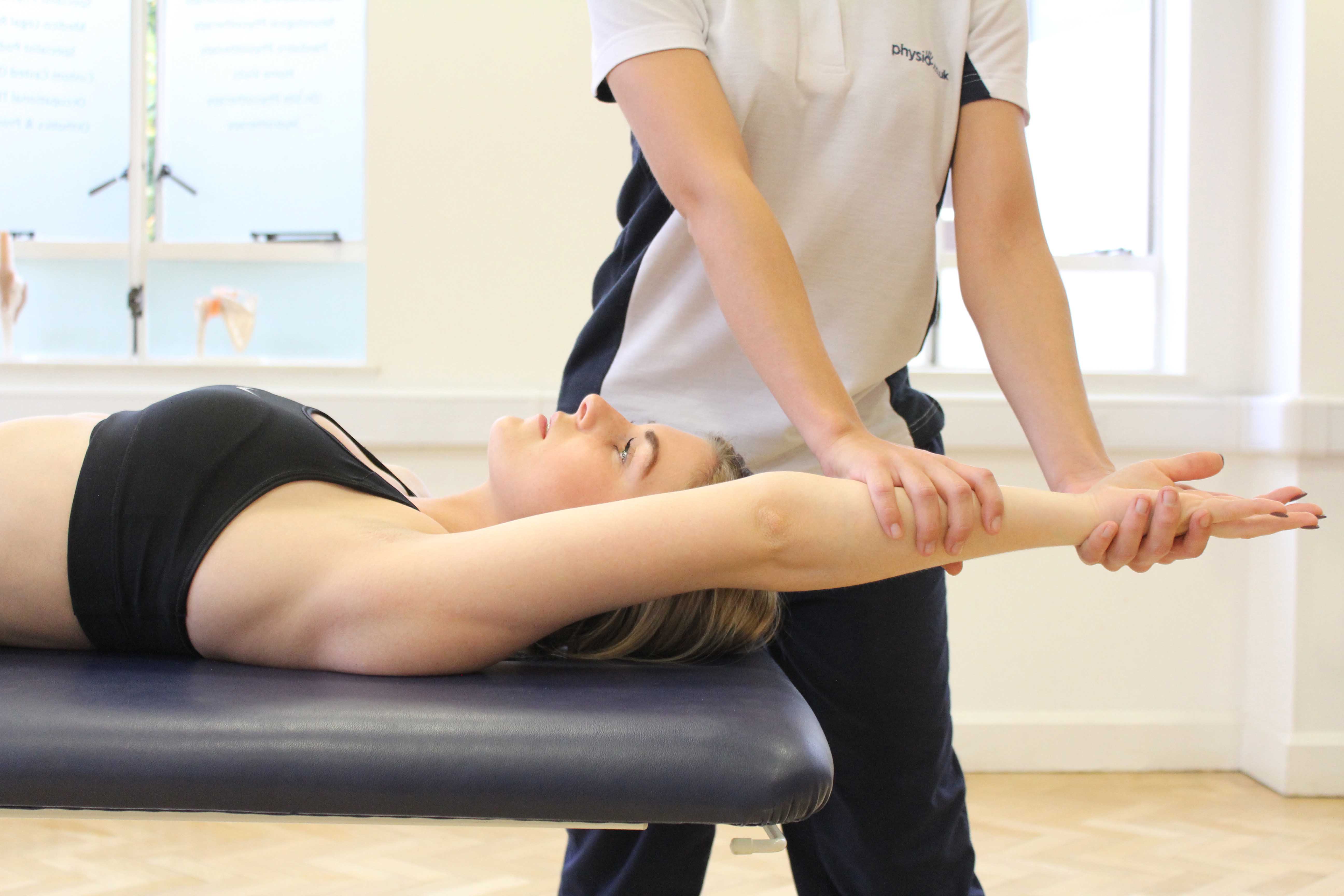
Some of the physiotherapy modalities we may use in the management and treatment of rotator cuff injuries includes: